Introduction
What is Bitcoin? Wikipedia defines bitcoin as:
[Bitcoin is] a form of electronic cash. It is a decentralized digital currency without a central bank or single administrator.
It’s a very simple statement. You might read this quickly and not really grasp what it means in a larger sense. The important stuff is in the last sentence. Bitcoin is distributed to users without the use of a central bank which might leave you with a lot of questions about how that is possible from a technical and more importantly an economic standpoint. If bitcoin isn’t issued by a central authority then who controls the production of the coins?
The following articles go over all of these questions:
- How does bitcoin work?
- What does the bitcoin network look like?
- What is bitcoin mining?
- What are bitcoin nodes?
- What is a bitcoin address?
- How many coins are there?
In order to answer “What is bitcoin?” we need to first understand what money is. There’s quite a few things that are never taught in school growing up, at least in the United States, and money is one of them. You were taught how to count it, and that there’s an entity called the Federal Reserve, but you weren’t exactly taught the history of it. A vast majority of individuals assume that every paper dollar is “backed” by an equivalent amount of gold. This is 100% false and hasn’t been the case since 1971.
So what is money then? There’s a plethora of youtube videos and articles out there describing the history of the US dollar, so I won’t get into that here. A list of videos on the history of money can be found here. Money, in it’s truest form, is a medium of exchange which allows individuals to conduct public and private business with each other. The fact that it is not backed by anything makes no difference. If the public trusts the currency, it will be used with no friction.
Sound Money
money [that is] not liable to sudden appreciation or depreciation in value : stable money; specifically : a currency based on or redeemable in gold
Webster’s Dictionary
The move away from the gold standard has caused an inflation in the price of goods and services in the United States. The value of the US dollar has dropped considerably since the 1900s due to quantitative easing.
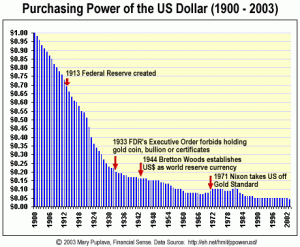
Inflation is fought by hedging against the US dollar. Strategies include diversifying your portfolio by investing in companies outside of the United States, putting some fiat money into precious metals, jewelry, and more recently bitcoin. By hedging your bets you protect yourself from some inflation. If the national inflation rate is 2.9% per year and you’ve invested 10% of your cash into other currencies/commodities – if those did well you offset that inflation by a little bit.
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin can be seen as an addition to your portfolio for longer term holders. Bitcoin can also be seen as a peer-to-peer currency which cuts out the middleman (banks). It is a new emerging asset class that was born in 2009 and has seen remarkable price growth. Bitcoin is more than that though, and it’s price is just the tip of the iceberg. Much like the US dollar of today, which is backed by nothing but trusting that the government won’t destroy it, bitcoin is also only backed by the trust that the system is open for everyone to see and the fact that it can’t be changed on a whim from it’s 21 million coin cap by any central authority thereby diluting and growing the coin pool. The mathematical model which secures bitcoin ensures that it can never be hacked (and has not been hacked to this day) – only exchanges which house bitcoin have been hacked due to exchange’s poor security models.
To learn more about Bitcoin’s other use cases, check out this article.